De-Asphalting – Application Overview
A de-asphalter separates asphalt from crude oil or bitumen using propane (or hexane) as a solvent.
The de-asphalter unit is usually placed after the vacuum distillation tower. A de-asphalter unit (SDA) separates asphalt from the feedstock based on differences in solubility. The products are then evaporated and steam stripped to recover the propane, which is recycled. De-asphalting also removes some sulphur and nitrogen compounds, metals, carbon residues and paraffins from the feedstock.
The output from the de-asphalter unit is de-asphalted oil (“DAO”) and asphalt.
| FLOW DIAGRAM | |||||
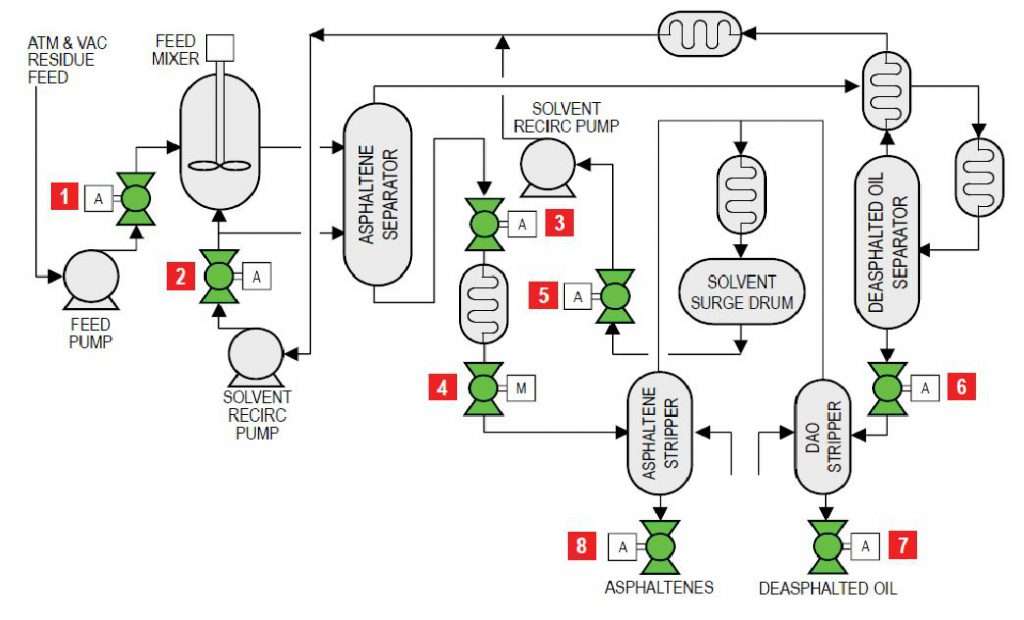 |
|||||
| Item | Applications | Temp range (°F) | Pressure (psi) | Size (in) | |
| 1 | Feed isolation | 200 – 500 | 400 – 900 | 4 – 16 | |
| 2 | Solvent circulating pump isolation | 200 – 500 | 400 – 900 | 4 – 16 | |
| 3 | Asphaltene separator emergency block valve | 200 – 500 | 400 – 900 | 4 – 16 | |
| 4 | Asphaltene separator isolation | 200 – 500 | 400 – 900 | 4 – 16 | |
| 5 | Solvent surge drum emergency block valve | 200 – 500 | 400 – 900 | 4 – 16 | |
| 6 | De-asphalted oil separator emergency block valve | 200 – 500 | 400 – 900 | 4 – 16 | |
| 7 | Asphalting stripper isolation | 200 – 500 | 400 – 900 | 4 – 16 | |
| 8 | De-asphalted oil stripper isolation | 200 – 500 | 400 – 900 | 4 – 16 | |








