Vacuum Distillation – Application Guide
Vacuum distillation works on the principle that boiling occurs when the vapor pressure of a liquid exceeds the ambient pressure. In vacuum distillation, the pressure above the reduced crude to be distilled is reduced to less than its vapor pressure, via vacuum and stripping steam, resulting on evaporation of gas oils starting with oils with the lowest boiling point. This process helps in recovery of valuable gas oils that are not separated by atmospheric distillation.
Pressures are typically as low as 10-40 mm of mercury (Hg) so as to limit the operating temperature to less than 370-380°C.
PROCESS OBJECTIVE
To recover valuable gas oils from reduced crude via vacuum distillation.
PRIMARY PROCESS TECHNIQUE
Reduce the hydrocarbon partial pressure via vacuum and stripping steam.
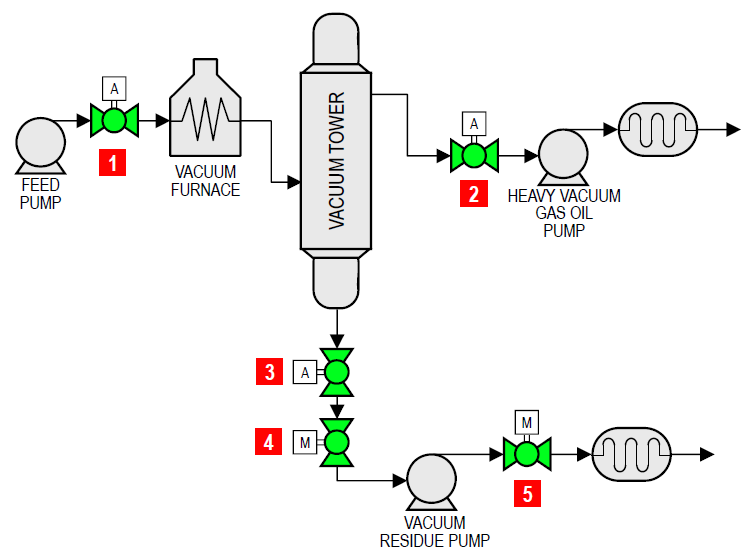
| FLOW DIAGRAM | |||||
 |
|||||
| Item | Applications | Temp range (°F) | Pressure (psi) | Size (in) | |
| 1 | Feed isolation | 200 – 320 | 100 – 200 | 6 – 10 | |
| 2 | Heavy vacuum gas oil pump emergency block valve | 200 – 320 | 0 – 20 | 4 – 8 | |
| 3 | Vacuum tower bottoms emergency block valve | 350 – 500 | 0 – 20 | 8 – 14 | |
| 4 | Vacuum bottoms pump isolation | 350 – 500 | 0 – 20 | 6 – 10 | |
| 5 | Vacuum bottoms exchanger isolation | 350 – 500 | 150 | 6 – 10 | |








